Embark on an intriguing exploration of the molar mass of silver bromide, a fascinating compound with a rich history and diverse applications. This journey will delve into its composition, properties, production, and the captivating role it plays in various industries, leaving you with a newfound appreciation for this remarkable substance.
Silver bromide, a compound of silver and bromine, boasts a unique set of characteristics that make it invaluable in fields ranging from photography to medicine. Its molar mass, a fundamental property, plays a crucial role in understanding its behavior and reactivity.
Molar Mass of Silver Bromide

In chemistry, molar mass refers to the mass of one mole of a substance. It’s a crucial concept for determining the amount of substance present in a given sample.
Calculating Molar Mass, Molar mass of silver bromide
The formula for calculating molar mass is:
Molar Mass = (Atomic Mass of Each Element × Number of Atoms of That Element) + …
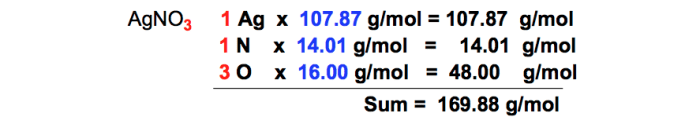
For silver bromide (AgBr), we need the atomic masses of silver (Ag) and bromine (Br) from the periodic table:
- Atomic mass of Ag: 107.87 u
- Atomic mass of Br: 79.90 u
Composition of Silver Bromide
Silver bromide is a chemical compound composed of two elements: silver and bromine. The chemical formula for silver bromide is AgBr.
Chemical Bonding in Silver Bromide
The chemical bonding in silver bromide is ionic. This means that the silver atom loses an electron to the bromine atom, resulting in the formation of a positively charged silver ion (Ag+) and a negatively charged bromide ion (Br-).
Molecular Structure of Silver Bromide
The molecular structure of silver bromide is cubic. The silver ions are arranged in a face-centered cubic lattice, and the bromide ions are arranged in a body-centered cubic lattice.
- Silver ions: Ag+
- Bromide ions: Br-
Applications of Silver Bromide
Silver bromide has played a pivotal role in various industries throughout history and continues to find applications in modern times.Historically, silver bromide’s most significant use was in photography. It was a key component in the development of photographic film and paper, allowing for the capture and reproduction of images.
The light-sensitive properties of silver bromide enabled it to react to light, forming an image on the film or paper. This technology revolutionized photography and made it accessible to the masses.In modern times, silver bromide continues to be used in various industries, including:
Medical Imaging
Silver bromide is used in the production of X-ray films. When exposed to X-rays, silver bromide reacts to form an image on the film, allowing medical professionals to diagnose and treat various medical conditions.
Industrial Applications
Silver bromide is utilized in the production of photochromic lenses, which change color when exposed to sunlight. These lenses are commonly found in sunglasses and other eyewear applications. Additionally, silver bromide is used in the manufacturing of photographic paper and film for industrial and commercial purposes.
Scientific Research
Silver bromide is employed in scientific research as a scintillator. When exposed to radiation, silver bromide emits light, which can be detected and analyzed to provide information about the radiation’s properties. This is useful in various scientific fields, such as nuclear physics and particle physics.
Silver bromide, a light-sensitive compound used in photography, has a molar mass of 187.77 g/mol. The concept of molar mass is essential in chemistry, as it allows us to determine the mass of a substance based on its molecular formula.
For instance, if you’re curious about the molar mass of silver bromide, you can easily find it by searching for ” zuku question of the day “.
Properties of Silver Bromide
Silver bromide, a light-sensitive compound, exhibits distinct physical and chemical properties that contribute to its applications in various fields. Understanding these properties is crucial for comprehending its behavior and utilization.
Physical Properties
Physically, silver bromide appears as a pale yellow or cream-colored solid. Its density is approximately 6.47 g/cm³, indicating a relatively high mass per unit volume. Silver bromide melts at a temperature of 432 °C, transitioning from a solid to a liquid state.
Chemical Properties
Chemically, silver bromide is a relatively stable compound. However, it undergoes reactions under specific conditions. Silver bromide is insoluble in water, indicating its low affinity for aqueous environments. However, it readily dissolves in solutions containing complexing agents like ammonia or thiosulfate, forming soluble complexes.
Comparison with Other Silver Halides
Comparing silver bromide to other silver halides, such as silver chloride and silver iodide, reveals similarities and differences. The following table summarizes their key properties:
| Property | Silver Chloride | Silver Bromide | Silver Iodide |
|---|---|---|---|
| Color | White | Pale Yellow | Yellow |
| Density (g/cm³) | 5.64 | 6.47 | 5.67 |
| Melting Point (°C) | 455 | 432 | 553 |
| Solubility in Water | Insoluble | Insoluble | Insoluble |
Production of Silver Bromide: Molar Mass Of Silver Bromide

Silver bromide can be produced through various methods, each involving specific chemical reactions.
Laboratory Synthesis
In a laboratory setting, silver bromide can be synthesized using the following steps:1.
-
-*Dissolve silver nitrate (AgNO3) in water
Prepare an aqueous solution of silver nitrate by dissolving it in distilled water.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
-*Add potassium bromide (KBr) solution
Slowly add a potassium bromide solution to the silver nitrate solution while stirring constantly.
-*Formation of silver bromide precipitate
A white precipitate of silver bromide (AgBr) will form as the two solutions react.
-*Filter and wash the precipitate
Filter the precipitate using a Buchner funnel and wash it thoroughly with distilled water to remove any impurities.
-*Dry the silver bromide
Transfer the washed precipitate to a petri dish and place it in an oven at a low temperature (around 50°C) to dry.
Clarifying Questions
What is the molar mass of silver bromide?
The molar mass of silver bromide is approximately 187.77 g/mol.
How is silver bromide used in photography?
Silver bromide is used in photography as a light-sensitive material in photographic film and paper.
What are the industrial applications of silver bromide?
Silver bromide is used in various industries, including medicine (X-ray imaging), electronics (photoresists), and manufacturing (plating).