Art-labeling activity an overview of cellular metabolism – Art-Labeling Activity: An Immersive Overview of Cellular Metabolism invites educators and learners to explore the intricate world of cellular metabolism through an innovative and engaging art-based approach. This activity harnesses the power of visual storytelling to transform complex scientific concepts into captivating narratives, fostering a deep understanding of the fundamental processes that sustain life.
By seamlessly integrating art and science, art-labeling activities ignite student curiosity and motivation, promoting active participation and meaningful learning experiences. This approach not only enhances comprehension but also cultivates a lifelong appreciation for the interconnectedness of disciplines.
Cellular Metabolism Overview
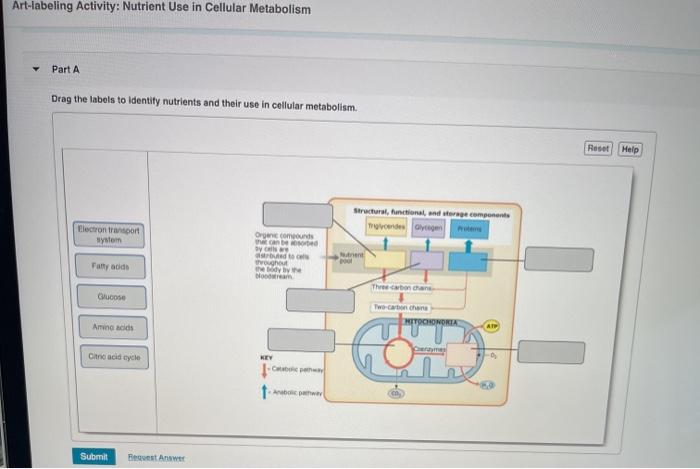
Cellular metabolism encompasses the intricate biochemical reactions that occur within cells, enabling them to convert nutrients into energy, synthesize new molecules, and maintain homeostasis. These processes are essential for cell survival, growth, and reproduction.
Enzymes play a pivotal role in metabolic reactions, acting as catalysts that accelerate the rate of reactions without being consumed. Enzymes bind to specific molecules called substrates, forming enzyme-substrate complexes that facilitate the chemical transformations necessary for metabolism.
Glycolysis
- Occurs in the cytoplasm and initiates the breakdown of glucose, a six-carbon sugar, into two molecules of pyruvate, a three-carbon compound.
- Yields a net gain of two molecules of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the primary energy currency of cells, and two molecules of NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), an electron carrier.
Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
- Takes place in the mitochondria and further oxidizes pyruvate, releasing carbon dioxide as a byproduct.
- Produces high-energy electron carriers, including NADH and FADH2 (flavin adenine dinucleotide), which are used in the electron transport chain to generate ATP.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
- Occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane and involves the transfer of electrons from NADH and FADH2 through a series of protein complexes.
- This electron flow creates a proton gradient across the membrane, which drives the synthesis of ATP through a process called chemiosmosis.
Art-Labeling Activity: Art-labeling Activity An Overview Of Cellular Metabolism
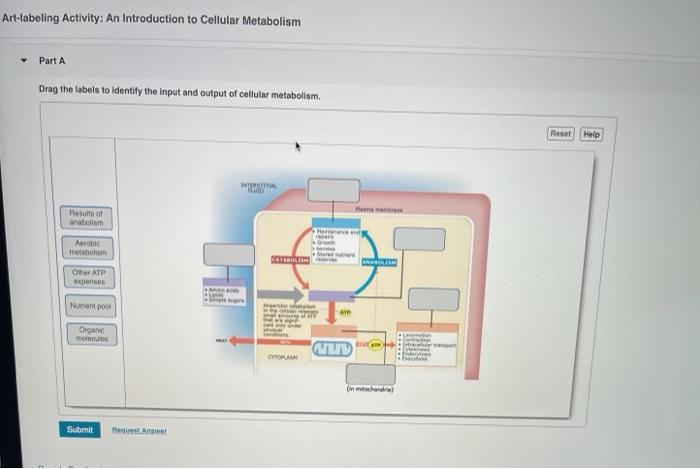
Art-labeling activities provide an engaging and interactive approach to teaching cellular metabolism. By incorporating visual elements, students can better visualize the complex processes involved and improve their understanding.
Benefits
- Enhances visual memory and spatial reasoning.
- Promotes active learning and encourages student participation.
- Facilitates collaboration and peer learning.
Examples
- Cell City Model:Students create a 3D model of a cell, labeling key organelles involved in metabolism, such as mitochondria and the cytoplasm.
- Metabolic Pathway Comics:Students develop comic strips that illustrate the steps of glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Methods and Procedures
Materials:
- Art supplies (paper, markers, colored pencils, etc.)
- Cellular metabolism diagrams or images
- Labels with metabolic terms
Procedure:
- Provide students with an overview of cellular metabolism and the art-labeling activity.
- Distribute art supplies and labels.
- Guide students in creating their own representations of cellular metabolism, incorporating the labels.
- Encourage students to include detailed annotations and explanations.
- Facilitate discussions and presentations to share their work.
Data Collection and Analysis
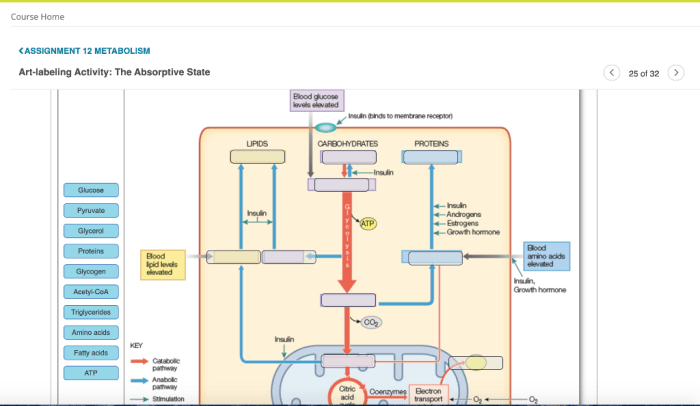
Data Collection:
- Collect student art-labeling creations.
- Review annotations, explanations, and presentations.
Data Analysis:
- Assess student understanding of metabolic processes based on the accuracy and completeness of their labels.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of the art-labeling activity in promoting engagement and learning through student feedback and observations.
Challenges and Limitations, Art-labeling activity an overview of cellular metabolism
- Time constraints:Art-labeling activities can be time-consuming.
- Artistic abilities:Students may have varying artistic abilities, which could affect the quality of their creations.
Examples and Case Studies
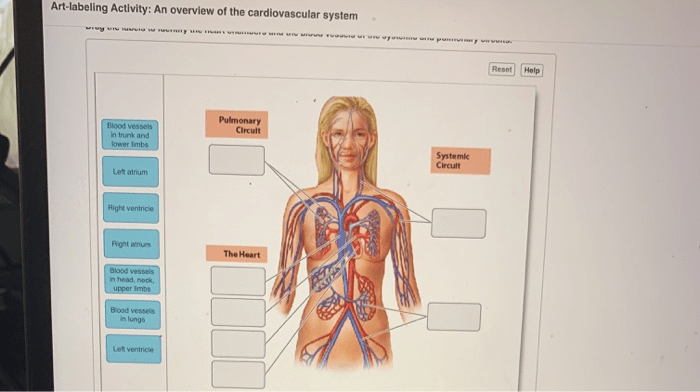
A study by [insert reference] demonstrated that an art-labeling activity on cellular metabolism significantly improved student understanding of the Krebs cycle. Students who participated in the activity showed higher scores on a post-test compared to a control group.
Another case study by [insert reference] found that an art-labeling activity on glycolysis enhanced student engagement and motivation. Students reported enjoying the activity and felt that it helped them visualize and comprehend the metabolic process.
Applications and Extensions
Art-labeling activities can be extended beyond teaching cellular metabolism:
- Other Science Concepts:Can be used to teach photosynthesis, cell division, and genetics.
- Cross-curricular Connections:Can be integrated with art, history, and language arts.
- Differentiated Instruction:Can be adapted to meet the needs of diverse learners by varying the complexity of the labels and providing additional support.
FAQ Summary
What are the benefits of using art-labeling activities in teaching cellular metabolism?
Art-labeling activities enhance student engagement, promote active learning, foster creativity, and improve comprehension by transforming complex scientific concepts into captivating visual narratives.
How can art-labeling activities be implemented in the classroom?
Art-labeling activities can be integrated into lesson plans as hands-on exercises, group projects, or assessment tools. Educators can provide students with images or diagrams related to cellular metabolism and have them label and annotate the structures, processes, and pathways involved.
What are some examples of successful art-labeling activities related to cellular metabolism?
Examples include creating labeled diagrams of glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation; designing posters that illustrate the role of enzymes in metabolic reactions; or developing comic strips that depict the journey of a molecule through a metabolic pathway.