Embark on a geometric adventure with lesson 2-3 two dimensional figures answer key, a definitive resource that unravels the mysteries of shapes that reside in a two-dimensional realm. Delve into the intricacies of triangles, squares, circles, and rectangles, as we explore their properties, unravel their characteristics, and uncover their applications in the world around us.
This comprehensive guide provides a thorough understanding of two-dimensional figures, empowering you with the knowledge to identify, measure, and utilize these geometric building blocks effectively. Prepare to expand your geometric horizons as we delve into the fascinating world of two-dimensional figures.
Lesson 2-3: Two-Dimensional Figures: Lesson 2-3 Two Dimensional Figures Answer Key
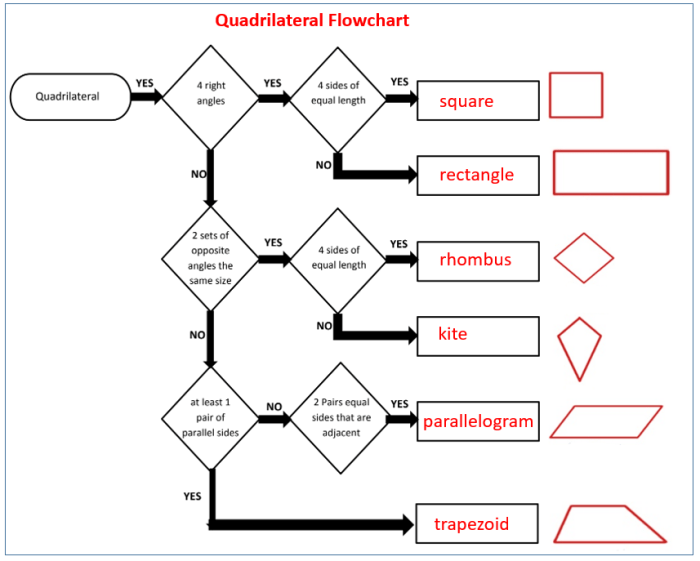
Two-dimensional figures are geometric shapes that have length and width but no thickness or height. They lie flat on a plane and can be defined by their shape, size, and area.
Examples of two-dimensional figures include triangles, squares, circles, and rectangles. These figures have different properties that distinguish them from one another, such as the number of sides, the length of the sides, and the presence of angles.
Identifying Two-Dimensional Figures
- Identify the shape of the figure: Determine if it is a triangle, square, circle, rectangle, or another shape.
- Count the number of sides: Two-dimensional figures can have three, four, or more sides.
- Examine the angles: Two-dimensional figures can have acute, right, or obtuse angles.
Measuring Two-Dimensional Figures
The area of a two-dimensional figure is the amount of space it occupies on a flat surface. The perimeter of a two-dimensional figure is the distance around its boundary.
Formulas for calculating the area and perimeter of common two-dimensional figures:
| Figure | Area | Perimeter |
|---|---|---|
| Triangle | (1/2)
|
sum of the lengths of all three sides |
| Square | side length2 | 4
|
| Circle | π
|
2π
|
| Rectangle | length
|
2
|
Applications of Two-Dimensional Figures, Lesson 2-3 two dimensional figures answer key
Two-dimensional figures have numerous applications in real-world scenarios, including:
- Architecture: Designing floor plans, walls, and roofs.
- Design: Creating logos, posters, and web graphics.
- Engineering: Designing bridges, airplanes, and other structures.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key characteristics of two-dimensional figures?
Two-dimensional figures are defined by their length and width, forming a flat surface with no height or depth. They possess properties such as shape, size, and area, which can be used to classify and identify different types of two-dimensional figures.
How do I calculate the area of a rectangle?
To calculate the area of a rectangle, multiply its length by its width. The formula for the area of a rectangle is: Area = Length x Width
What is the difference between a square and a rectangle?
A square is a specific type of rectangle where all four sides are equal in length. In contrast, a rectangle has two pairs of equal sides, but the length and width can differ.