Label the muscle spindle structures. – Labeling the muscle spindle structures is a crucial step in understanding the intricate workings of the muscular system. These specialized sensory organs play a pivotal role in maintaining muscle tone, regulating movement, and providing proprioceptive feedback to the central nervous system.
This comprehensive guide delves into the anatomy and function of the muscle spindle, unraveling its complex interplay with the nervous system.
As we embark on this journey, we will meticulously identify the intrafusal and extrafusal muscle fibers, sensory nerve endings, and gamma motor neurons that orchestrate the muscle spindle’s remarkable functions.
Define the Muscle Spindle
A muscle spindle is a sensory organ located within skeletal muscles that detects changes in muscle length and contributes to the regulation of muscle tone.
Identify the Structures of the Muscle Spindle
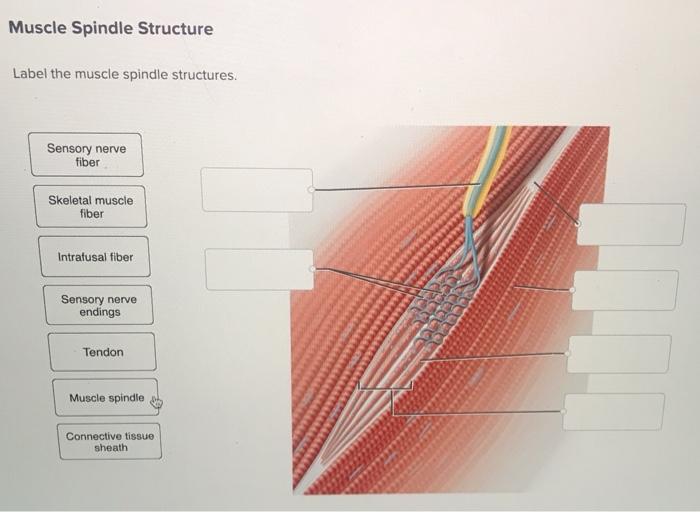
The muscle spindle consists of the following structures:
- Intrafusal muscle fibers:These are specialized muscle fibers within the muscle spindle that are responsible for sensing changes in muscle length.
- Extrafusal muscle fibers:These are the regular muscle fibers that surround the muscle spindle.
- Sensory nerve endings:There are two types of sensory nerve endings in the muscle spindle: primary and secondary. Primary nerve endings are located in the central region of the spindle and are highly sensitive to changes in muscle length. Secondary nerve endings are located at the ends of the spindle and are less sensitive to changes in muscle length.
- Gamma motor neurons:These are motor neurons that innervate the intrafusal muscle fibers. They control the sensitivity of the muscle spindle by adjusting the tension of the intrafusal muscle fibers.
Explain the Sensory Function of the Muscle Spindle: Label The Muscle Spindle Structures.
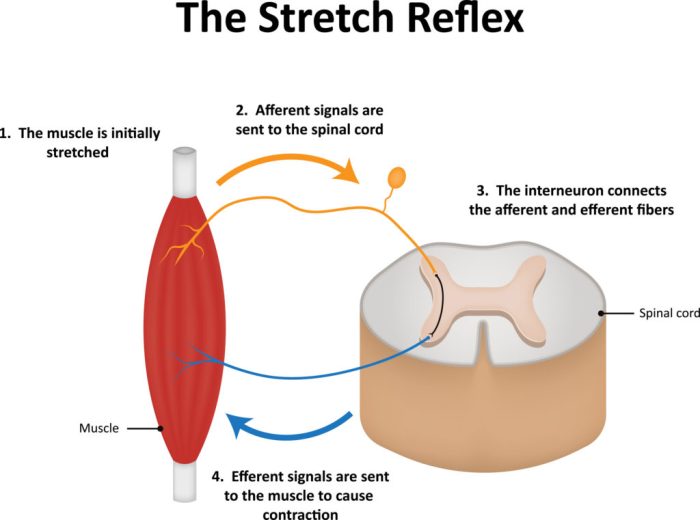
When the muscle is stretched, the intrafusal muscle fibers are stretched as well. This stretching activates the sensory nerve endings, which send signals to the spinal cord. The spinal cord then sends signals back to the muscle to adjust its length and maintain muscle tone.
Elaborate on the Motor Function of the Muscle Spindle
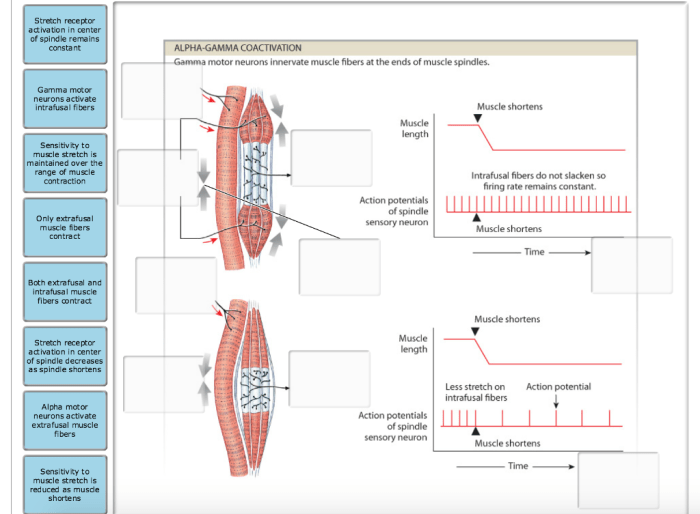
The gamma motor neurons regulate the sensitivity of the muscle spindle. When the gamma motor neurons are activated, they increase the tension of the intrafusal muscle fibers, which makes the muscle spindle more sensitive to changes in muscle length. This helps to maintain muscle tone and prevent muscle atrophy.
Illustrate the Clinical Significance of the Muscle Spindle
Muscle spindle dysfunction can lead to a variety of muscle disorders, including muscle weakness, muscle atrophy, and muscle spasms. The muscle spindle is also used to assess neuromuscular disorders, such as myasthenia gravis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Questions Often Asked
What is the primary function of the muscle spindle?
The muscle spindle serves as a sensory organ that detects changes in muscle length, providing proprioceptive feedback to the central nervous system.
How do sensory nerve endings contribute to the function of the muscle spindle?
Sensory nerve endings, particularly the primary and secondary endings, transmit information about muscle length changes to the spinal cord, enabling the brain to maintain muscle tone and regulate movement.
What is the role of gamma motor neurons in the muscle spindle?
Gamma motor neurons regulate the sensitivity of the muscle spindle by adjusting the tension of the intrafusal muscle fibers, influencing the threshold for detecting muscle length changes.