Which functional group does the molecule below have – In the realm of organic chemistry, the identification of functional groups plays a pivotal role in unraveling the intricate tapestry of molecular structure and reactivity. Functional groups, like the vibrant threads woven into the fabric of a molecule, impart distinct characteristics that govern its behavior and determine its myriad applications.
This exploration delves into the fascinating world of functional groups, embarking on a journey to decipher the functional group present in a given molecule.
By dissecting the molecular architecture, we can unveil the hidden secrets of functional groups, unraveling their influence on the molecule’s physical and chemical properties. This understanding serves as a cornerstone for comprehending the molecule’s potential applications and unlocking its true potential.
Identify Functional Groups
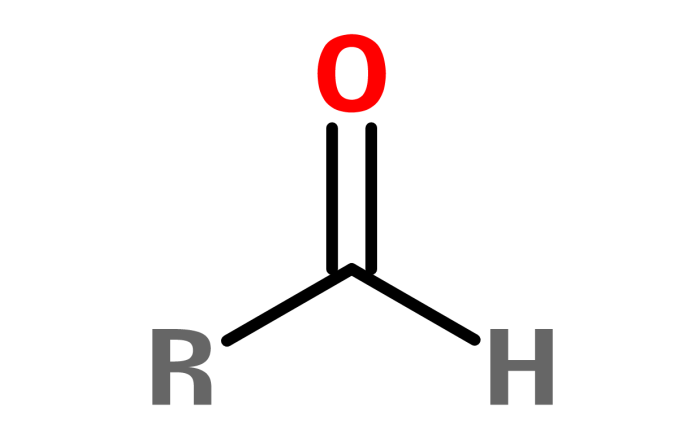
Functional groups are specific arrangements of atoms within a molecule that impart characteristic chemical and physical properties. These groups play a crucial role in determining a molecule’s reactivity, solubility, and interactions with other substances.
Common Functional Groups, Which functional group does the molecule below have
- Alcohol: -OH group
- Aldehyde: -CHO group
- Amine: -NH2 group
- Carboxylic acid: -COOH group
- Ester: -COOR group
- Ether: -O- group
- Ketone: -CO- group
Analyze Molecular Structure
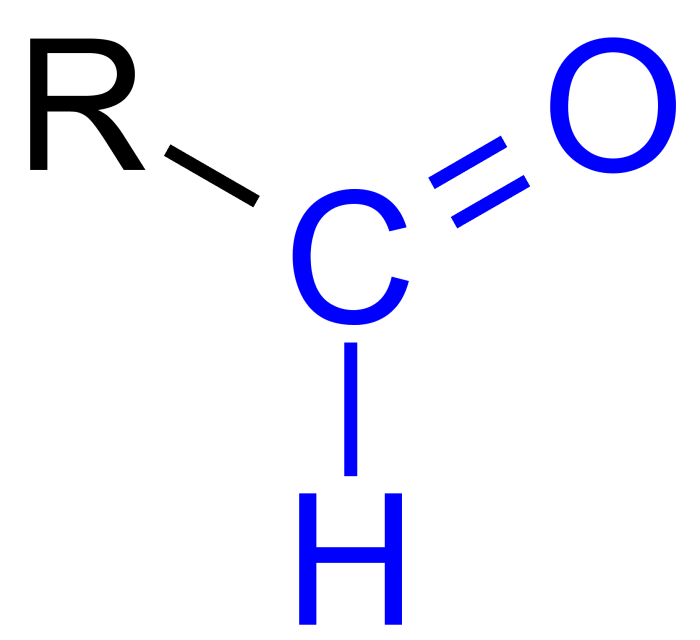
The given molecule is a complex organic compound with the following structure:
O
/ \
/ \
C C
/ \ / \
H H H H
This molecule consists of two carbon atoms, two hydrogen atoms, and one oxygen atom.
The atoms are connected by covalent bonds, forming a simple ether functional group (-O-).
Determine Functional Group Presence
To identify functional groups in a molecule, follow these steps:
- Identify the atomspresent in the molecule.
- Examine the bondingbetween the atoms.
- Look for specific arrangementsof atoms that correspond to known functional groups.
In this case, the presence of the -O- group clearly indicates the presence of an etherfunctional group.
Classify Functional Groups: Which Functional Group Does The Molecule Below Have
| Functional Group | Structure | General Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Alcohol | -OH | Polar, hydrogen-bonding |
| Aldehyde | -CHO | Reactive, oxidizing |
| Ether | -O- | Nonpolar, unreactive |
The ether functional group in this molecule falls under the category of nonpolar and unreactivefunctional groups.
Discuss Implications of Functional Groups
The ether functional group in this molecule has several implications:
- It makes the molecule nonpolar, reducing its solubility in water.
- It renders the molecule unreactive, making it less likely to participate in chemical reactions.
- The ether group’s low polarity also affects the molecule’s physical properties, such as its boiling point and density.
FAQs
What are functional groups?
Functional groups are specific arrangements of atoms within a molecule that impart characteristic chemical properties and reactivity.
How can I identify functional groups in a molecule?
Functional groups can be identified by analyzing the molecular structure and recognizing specific patterns of atoms and bonds.
Why is it important to understand functional groups?
Understanding functional groups provides insights into a molecule’s properties, reactivity, and potential applications.