Bacteria and resistance what is mrsa worksheet answers? This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of bacterial resistance, with a particular focus on the notorious MRSA, providing a thorough understanding of its significance, causes, transmission, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and future research directions.
Antibiotic resistance has emerged as a pressing concern in healthcare, and MRSA stands as a prime example of this phenomenon. This guide aims to equip readers with a comprehensive understanding of MRSA, empowering them to navigate the complexities of bacterial resistance and contribute to effective infection control measures.
Introduction
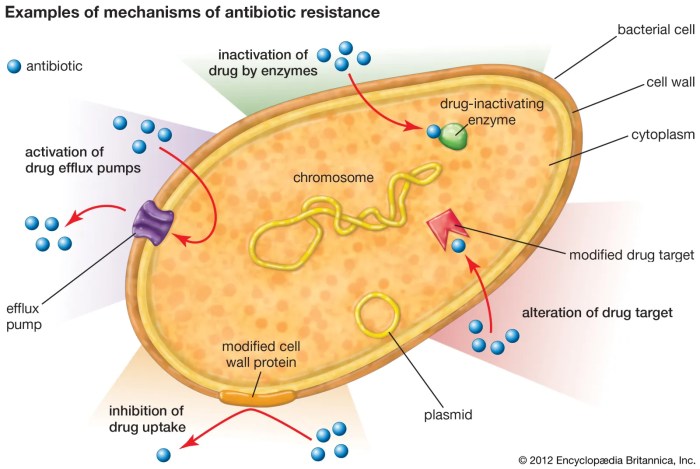
Bacteria play a crucial role in healthcare, as they can cause infections that require antibiotic treatment. However, the emergence of antibiotic resistance has become a significant challenge, threatening the effectiveness of antibiotics and complicating the treatment of bacterial infections. One of the most concerning antibiotic-resistant bacteria is Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus(MRSA), which has a significant impact on public health worldwide.
Causes and Transmission of MRSA
Bacteria develop resistance to antibiotics through various mechanisms, including gene mutation and horizontal gene transfer. MRSA specifically develops resistance to methicillin, a type of antibiotic, through the acquisition of a gene that produces a modified penicillin-binding protein. This protein reduces the affinity of methicillin and other beta-lactam antibiotics, rendering them ineffective against MRSA.
MRSA can be transmitted through direct contact with an infected person or by touching contaminated surfaces or objects. Healthcare settings, such as hospitals and nursing homes, are common sources of MRSA transmission, but community-associated MRSA (CA-MRSA) has also emerged, causing infections outside healthcare facilities.
Diagnosis and Treatment of MRSA
MRSA infections can be diagnosed through various methods, including culture and susceptibility testing, which involves growing the bacteria in a laboratory and determining their antibiotic sensitivity. Molecular diagnostic techniques, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), can also be used to detect MRSA rapidly.
The treatment of MRSA infections requires the use of antibiotics that are effective against methicillin-resistant bacteria. These antibiotics include vancomycin, linezolid, and daptomycin. In some cases, combination therapy with multiple antibiotics may be necessary to achieve optimal outcomes.
Prevention and Control of MRSA
Preventing and controlling MRSA infections is essential in both healthcare settings and the community. Effective measures include:
- Hand hygiene: Regular and thorough handwashing with soap and water or alcohol-based hand sanitizers is crucial in preventing the spread of MRSA.
- Environmental cleaning: Cleaning and disinfecting surfaces and equipment in healthcare settings and public areas can help reduce the risk of MRSA transmission.
- Antibiotic stewardship: Judicious use of antibiotics is essential to prevent the development and spread of antibiotic resistance, including MRSA.
Challenges and Future Directions, Bacteria and resistance what is mrsa worksheet answers
Combating MRSA infections poses several challenges, including the emergence of new resistant strains and the limited number of effective antibiotics available. Research is ongoing to develop new antibiotics, vaccines, and other innovative approaches to address MRSA infections.
Future directions in MRSA research include:
- Developing new antibiotics with novel mechanisms of action to overcome resistance.
- Investigating the role of the microbiome in MRSA colonization and infection.
- Exploring the use of bacteriophages, viruses that specifically target bacteria, as a potential treatment for MRSA infections.
Quick FAQs: Bacteria And Resistance What Is Mrsa Worksheet Answers
What is MRSA?
MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) is a strain of bacteria that has developed resistance to commonly used antibiotics, making it more difficult to treat infections.
How is MRSA transmitted?
MRSA can be transmitted through direct contact with an infected person or by touching contaminated surfaces. It is commonly found in healthcare settings, but community-acquired MRSA infections are also on the rise.
What are the symptoms of an MRSA infection?
Symptoms of an MRSA infection can vary depending on the location and severity of the infection. Common symptoms include skin infections (such as boils or abscesses), respiratory infections (such as pneumonia), and bloodstream infections.
How is MRSA treated?
Treatment for MRSA infections typically involves the use of antibiotics that are specifically effective against MRSA. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to drain abscesses or remove infected tissue.
How can I prevent MRSA infections?
To prevent MRSA infections, it is essential to practice good hygiene, including frequent handwashing, covering wounds, and avoiding contact with infected individuals. In healthcare settings, strict adherence to infection control protocols is crucial.