Welcome to the animal cell coloring answer key biology corner, where the vibrant world of cells comes alive! Coloring animal cell diagrams is not just a fun activity but also a powerful educational tool that unlocks the mysteries of cell biology.
Dive into this comprehensive guide as we explore the intricate structures, functions, and significance of animal cells.
This engaging resource provides a step-by-step guide to coloring animal cell diagrams, empowering you to visualize and understand the complex inner workings of these fundamental units of life. Discover the purpose and benefits of coloring activities in education, and gain insights into the fascinating differences between animal and plant cells.
Animal Cell Coloring Activity
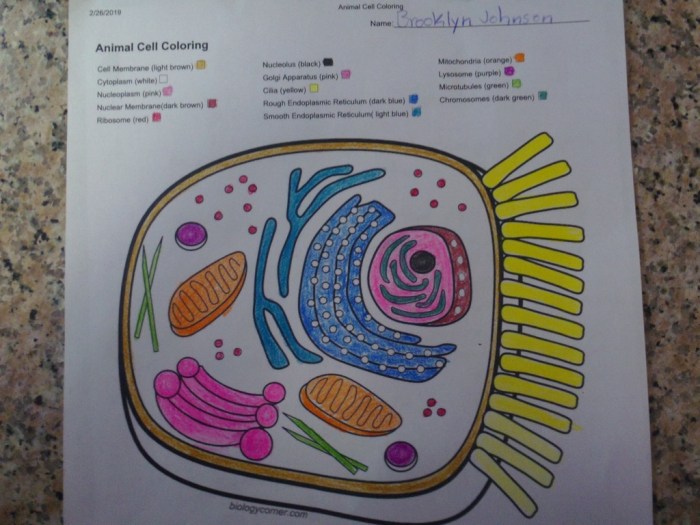
Coloring animal cell diagrams is a valuable educational tool that helps students visualize and understand the complex structures of these cells. By assigning different colors to specific cell components, students can better differentiate and identify these structures, enhancing their comprehension of cell biology.
Moreover, coloring activities provide a hands-on and engaging approach to learning, fostering student interest and retention. The act of coloring reinforces the visual representation of cell structures, making it easier for students to recall and apply their knowledge in various contexts.
Step-by-Step Guide to Coloring an Animal Cell Diagram
- Gather necessary materials: animal cell diagram, colored pencils or markers, and a color-coded key.
- Identify the different cell structures using the color-coded key.
- Color each structure according to the corresponding color in the key.
- Pay attention to the details and boundaries of each structure to ensure accurate representation.
- Use different shades and tones of colors to highlight specific features and differentiate between similar structures.
Animal Cell Structures
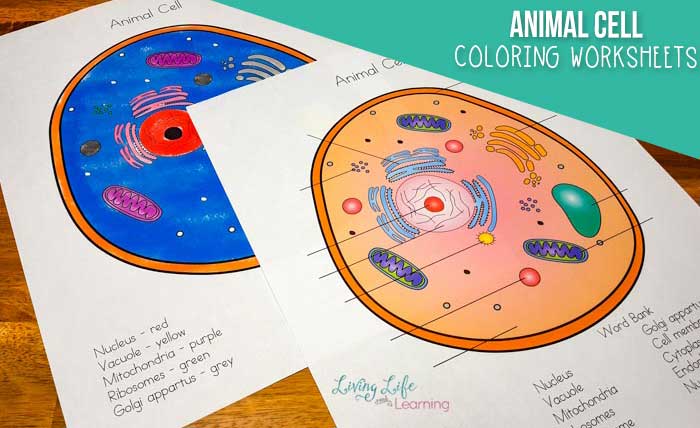
Major Structures of an Animal Cell, Animal cell coloring answer key biology corner
- Cell Membrane:A thin, flexible boundary that surrounds the cell, regulating the movement of substances in and out.
- Cytoplasm:A jelly-like substance that fills the cell, containing organelles and other cell components.
- Nucleus:A membrane-bound organelle that houses the cell’s genetic material (DNA).
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER):A network of membranes that folds and transports proteins.
- Golgi Apparatus:A series of flattened sacs that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins.
- Lysosomes:Membrane-bound organelles that contain digestive enzymes to break down waste and cellular debris.
- Mitochondria:Bean-shaped organelles that generate energy for the cell.
- Ribosomes:Small organelles that synthesize proteins.
- Centrosomes:Organelles that organize microtubules during cell division.
Comparison to Plant Cells
- Animal cells lack a cell wall and chloroplasts, unlike plant cells.
- Animal cells have centrioles, which are absent in plant cells.
- Animal cells generally have a smaller central vacuole compared to plant cells.
Coloring Key
The following color-coded key provides the appropriate colors for different animal cell structures:
| Structure | Color | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Membrane | Blue | Represents a semipermeable barrier. |
| Cytoplasm | Light Pink | Reflects its gel-like consistency. |
| Nucleus | Dark Blue | Signifies the importance of genetic material. |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | Red | Indicates its role in protein synthesis. |
| Golgi Apparatus | Green | Represents its function in packaging and secretion. |
| Lysosomes | Purple | Symbolizes their digestive role. |
| Mitochondria | Orange | Reflects their energy-producing function. |
| Ribosomes | Yellow | Highlights their role in protein synthesis. |
| Centrosomes | Gray | Represents their involvement in cell division. |
Interactive Table
| Structure | Description | Color |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Membrane | Regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell. | Blue |
| Cytoplasm | Jelly-like substance that fills the cell and contains organelles. | Light Pink |
| Nucleus | Houses the cell’s genetic material (DNA). | Dark Blue |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | Network of membranes that folds and transports proteins. | Red |
| Golgi Apparatus | Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins. | Green |
| Lysosomes | Contain digestive enzymes to break down waste and cellular debris. | Purple |
| Mitochondria | Generate energy for the cell. | Orange |
| Ribosomes | Synthesize proteins. | Yellow |
| Centrosomes | Organize microtubules during cell division. | Gray |
Additional Resources
- Khan Academy: Plasma Membrane
- Nature: The Endoplasmic Reticulum: Its Structure and Functions
- ScienceDirect: Lysosomes: Their Role in Cellular Aging and Age-Related Disease
Helpful Answers: Animal Cell Coloring Answer Key Biology Corner
What is the purpose of coloring animal cell diagrams?
Coloring animal cell diagrams enhances visual understanding, aids in memorization, and promotes engagement in learning about cell biology.
How does coloring contribute to educational purposes?
Coloring activities stimulate creativity, improve hand-eye coordination, and reinforce scientific concepts through visual representation.
What are the key structures of an animal cell?
Major structures include the nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, and lysosomes, each with specific functions.
How do animal cells differ from plant cells?
Animal cells lack a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large central vacuole, while they possess centrioles, which are absent in plant cells.
