Embarking on an exploration of reactions in solution lab mcgraw hill, this guide delves into the intricacies of chemical reactions occurring in liquid mediums, shedding light on their types, influencing factors, and practical applications.
From acid-base interactions to redox reactions, this comprehensive resource unravels the fundamental principles governing these reactions, empowering learners with a thorough understanding of solution chemistry.
Types of Reactions in Solution: Reactions In Solution Lab Mcgraw Hill
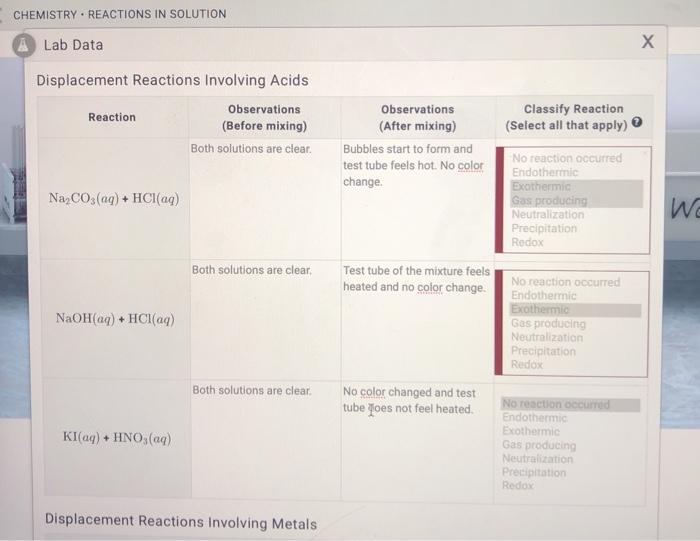
Chemical reactions in solution involve the interaction of ions or molecules in a liquid medium. These reactions can be classified into various types based on the nature of the reactants and products.
Acid-Base Reactions
Acid-base reactions involve the transfer of protons (H+ ions) between acids and bases. Acids donate protons, while bases accept them. The strength of an acid or base is determined by its ability to donate or accept protons, respectively.
Precipitation Reactions
Precipitation reactions occur when two solutions containing ions combine to form an insoluble solid precipitate. These reactions are often used to separate and purify substances or to synthesize new compounds.
Gas-Evolution Reactions
Gas-evolution reactions produce a gas as one of the products. These reactions can be used to generate gases for various purposes, such as inflating balloons or producing fuels.
Redox Reactions
Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between reactants. Oxidation refers to the loss of electrons, while reduction refers to the gain of electrons. Redox reactions are important in many biological and industrial processes.
Factors Affecting Reaction Rates
The rate of a chemical reaction is influenced by several factors, including:
Concentration, Reactions in solution lab mcgraw hill
The concentration of the reactants affects the frequency of collisions between them, which in turn affects the reaction rate. Higher concentrations lead to faster reaction rates.
Temperature
Increasing the temperature of a reaction system provides more energy to the reactants, which increases the likelihood of successful collisions and faster reaction rates.
Catalysts
Catalysts are substances that increase the rate of a reaction without being consumed themselves. They provide an alternative pathway for the reaction to occur, lowering the activation energy and speeding up the process.
Inhibitors
Inhibitors are substances that decrease the rate of a reaction. They can interfere with the collision process or bind to the reactants, reducing their reactivity.
Equilibrium in Solution
Chemical equilibrium occurs when the forward and reverse reactions of a reversible reaction proceed at equal rates. At equilibrium, the concentrations of the reactants and products remain constant.
Factors that Shift Equilibrium
The equilibrium position can be shifted by changing the conditions of the system, such as:
Concentration
Changing the concentration of reactants or products can shift the equilibrium towards the side that consumes or produces the added component.
Temperature
Changing the temperature can shift the equilibrium towards the side that is favored by the temperature change.
Pressure
For reactions involving gases, changing the pressure can shift the equilibrium towards the side with fewer moles of gas.
Applications of Equilibrium Principles
Equilibrium principles are used in various applications, including:
Buffer solutions
Buffers resist changes in pH by maintaining a constant concentration of hydrogen ions.
Solubility
The solubility of a substance is determined by the equilibrium between the solid and dissolved states.
Complexation
Equilibrium principles are used to understand the formation and stability of complexes between metal ions and ligands.
FAQ Resource
What are the different types of reactions in solution?
Reactions in solution can be categorized into acid-base reactions, precipitation reactions, gas-evolution reactions, and redox reactions.
How does temperature affect reaction rates?
Temperature plays a crucial role in reaction rates, with higher temperatures generally leading to faster reactions due to increased molecular motion and collision frequency.
What is the significance of equilibrium in solution?
Equilibrium in solution represents a state of balance where the forward and reverse reactions occur at equal rates, resulting in no net change in the concentrations of reactants and products.